GIS Software Unveiled: Navigating the Geospatial Revolution
In an age where data is the lifeblood of decision-making, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software emerges as an indispensable tool, seamlessly blending the digital world with the real one. At its core, GIS is a sophisticated framework that captures, stores, analyzes, and visualizes geospatial data. But it’s far more than just a digital map; it’s a transformative technology that transcends industries and empowers us to make informed choices, from city planning to environmental conservation and beyond.
The Geospatial Revolution
The impact of GIS software extends far beyond its definition. It’s the digital cartographer guiding urban planners to design smarter, greener cities. It’s the ecologist tracking animal migrations, the farmer optimizing crop yields, and the logistics manager streamlining supply chains. It’s the tool that makes sense of our world’s complex tapestry, stitching together data points, coordinates, and locations to tell a powerful story.
In this article, we’ll delve deep into the world of GIS software, exploring its myriad applications, benefits, and future possibilities. We’ll uncover how GIS isn’t just a tool; it’s a key that unlocks the doors to a more data-driven, efficient, and sustainable future. Join us on this journey to understand the heart of GIS and its impact on industries far and wide.
What is GIS Software?
GIS software, short for Geographic Information System, is a powerful technological solution with a primary purpose: to capture, manage, analyze, and interpret geospatial data. At its core, GIS serves as the bridge between the physical world and the digital realm, allowing us to make sense of our surroundings in ways previously unimagined. Its significance lies in its ability to facilitate data visualization and analysis in a spatial context. By integrating various layers of information on maps, GIS enables us to explore relationships, patterns, and trends that might remain hidden in traditional data tables. GIS tools not only capture geospatial data but also store and organize it efficiently, making it readily accessible for in-depth analysis. They empower professionals across industries, from urban planners to environmental scientists, to harness the power of location-based data, resulting in more informed decisions and comprehensive insights into our world.
Key Features of GIS Software
GIS software offers a versatile toolbox of features and functionalities that cater to a wide range of needs. Among its key attributes, map creation takes center stage. With GIS, you can craft detailed, customized maps that combine various data layers to create visually informative representations of geographic information. Spatial analysis, another essential feature, enables users to scrutinize and interpret data within a geographical context, uncovering valuable insights for informed decision-making.
Data visualization is a hallmark of GIS, allowing for the clear and intuitive presentation of complex spatial data. Through vivid maps, charts, and graphs, GIS transforms raw numbers into a visually comprehensible format. Additionally, data editing capabilities permit users to modify and update geographic data, ensuring that the information remains accurate and up-to-date.
GIS software doesn’t merely provide a passive representation of data; it empowers users to engage with their information in dynamic and impactful ways. These features collectively make GIS an indispensable tool in diverse fields, from urban planning and environmental management to logistics and beyond.
Diverse Applications of GIS Software Across Industries
Urban Planning: City and regional planners use GIS to assess land use, infrastructure, and transportation systems. It aids in designing sustainable and efficient cities, optimizing traffic flow, and managing public spaces.
Environmental Management: GIS is crucial for tracking and managing environmental data, including air and water quality, conservation efforts, and disaster response. It helps organizations monitor and mitigate the impact of climate change and natural disasters.
Real Estate and Property Management: Real estate professionals use GIS to analyze property values, zoning regulations, and demographic data. It assists in site selection, land development, and understanding market trends.
Healthcare: Healthcare organizations use GIS to analyze the spread of diseases, plan healthcare facility locations, and optimize emergency response routes. GIS also plays a role in epidemiology and public health research.
Agriculture: Farmers and agronomists utilize GIS to optimize crop management, including soil analysis, irrigation planning, and pest control. It aids in maximizing agricultural yields and minimizing resource use.
Natural Resource Management: Forestry, mining, and fisheries industries use GIS for resource planning and management. It helps in tracking the distribution of resources, ensuring sustainable use, and minimizing environmental impact.
Transportation and Logistics: GIS is crucial for route planning, vehicle tracking, and optimizing supply chain logistics. It enhances the efficiency of transportation and delivery services.
Archaeology and Cultural Heritage: Archaeologists and cultural preservationists use GIS to map historical sites, artifacts, and cultural resources. It aids in research, conservation, and heritage protection.
Emergency Services: Police, fire departments, and emergency response teams utilize GIS for location-based decision-making during emergencies. It helps in allocating resources, planning evacuation routes, and managing disaster response.
Natural Disasters and Crisis Management: GIS plays a vital role in monitoring and responding to natural disasters, such as hurricanes, wildfires, and earthquakes. It assists in disaster preparedness, response, and recovery efforts.
Retail and Marketing: Businesses use GIS for location-based marketing, site selection for new stores, and analyzing customer demographics to target marketing campaigns effectively.
Tourism and Recreation: GIS is used to create interactive maps for tourists, hikers, and outdoor enthusiasts. It helps plan recreational activities and highlight points of interest.
Selecting the Right GIS Software
The landscape of GIS mapping software is diverse and expansive, catering to a wide range of professionals from various industries. From globally recognized platforms like ESRI ArcGIS, known for its comprehensive and advanced features, to open-source alternatives like QGIS that offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness, and user-centric solutions like Smappen, finding the ideal tool that perfectly suits your needs can be challenging.
Choosing the right GIS software is a pivotal decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of your operations. Whether you’re a business looking to integrate GIS into your workflow or an individual seeking a personal GIS solution, here are some essential tips to help you make an informed choice.
First and foremost, consider the cost of the GIS software. Different GIS tools come with various pricing structures, and it’s crucial to align the cost with your budget. For businesses, it’s important to assess the return on investment (ROI) that the software can offer. Often, the cost of GIS software is justifiable by the efficiency gains and data-driven insights it provides.
Compatibility is another critical factor. Ensure that the GIS software you choose can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems and databases. Compatibility issues can lead to data silos and hinder the flow of information within your organization.
Scalability is equally important, especially for businesses with growth ambitions. The GIS software you select should be capable of expanding with your needs. It should accommodate larger datasets, increased user numbers, and the evolving complexity of your spatial analysis requirements.
By keeping these factors in mind and conducting thorough research, you can find the GIS software that best suits your unique needs, ensuring that you make the most of this invaluable technology.
Best GIS Mapping Tools
Here, we compare some of the leading GIS mapping tools in the market—ESRI ArcGIS, QGIS, and Smappen—highlighting their key features, use cases, and unique advantages to help users and businesses determine which tool best meets their needs.
ESRI ArcGIS
Key Features:
- Comprehensive suite of integrated applications
- Advanced spatial analysis, data management, and mapping
- Real-time GIS capabilities with location-based analytics
- Extensive support and training resources
Advantages: ESRI ArcGIS is renowned for its extensive functionality and integration capabilities, making it a popular choice among large enterprises and professional GIS users. It offers powerful tools for 3D GIS, real-time spatial analysis, and robust data visualization. Its widespread use in industries such as government, public safety, and utilities makes it a reliable standard for complex GIS projects.
QGIS
Key Features:
Open-source with a flexible plugin architecture
Supports a wide range of raster and vector formats
Strong community support and frequent updates
Cross-platform compatibility (Windows, Mac, Linux)
Advantages: QGIS stands out for its accessibility and no-cost entry point, ideal for students, individual professionals, and small to medium businesses. It provides a strong suite of tools for data editing, processing, and analysis, and its open-source nature allows for extensive customization and integration with third-party plugins, fostering a vibrant community of users and developers.
Smappen
Key Features:
User-friendly online interface suitable for non-experts
Specialized in creating, managing, and visualizing catchment areas on a personalized map
Access to up-to-date demographic data from various countries
Flexible subscription model with no long-term commitment
Advantages: Smappen is particularly beneficial for businesses that require GIS mapping tools with minimal learning curve and immediate deployment. It is especially adept at market analysis and network optimization, making it ideal for franchises and retail chains. The tool’s focus on demographic data and ease of use supports quick decision-making and effective marketing strategies.
Why Smappen Stands Out in GIS Software
Smappen, a leading name in the realm of GIS software, distinguishes itself by offering a comprehensive and user-friendly solution for businesses and individuals alike. What sets Smappen apart is its commitment to providing a seamless and educational experience for its users. The team’s responsive support and close engagement with clients make it an ideal choice for those seeking an intuitive GIS software solution.
Smappen also offers flexible pricing through a monthly subscription model, eliminating the need for long-term commitments. This affordability, combined with the software’s user-friendliness, ensures a quick learning curve and minimal training requirements, making it accessible to users at all levels of expertise.
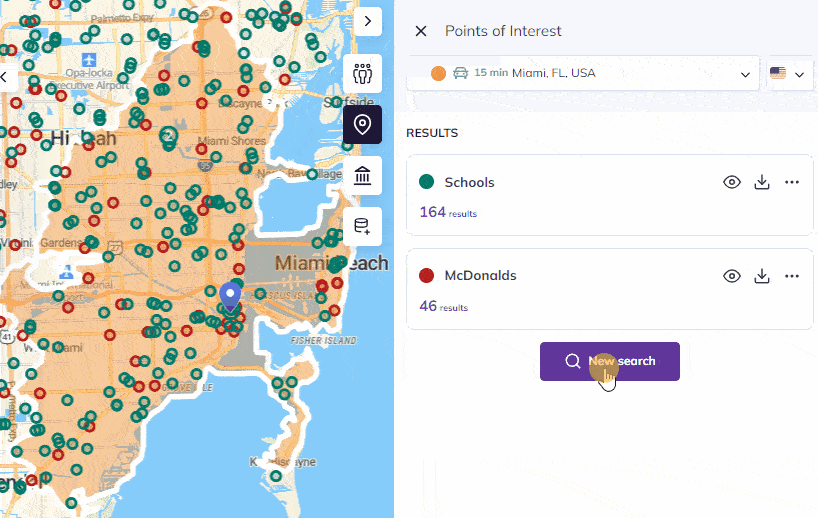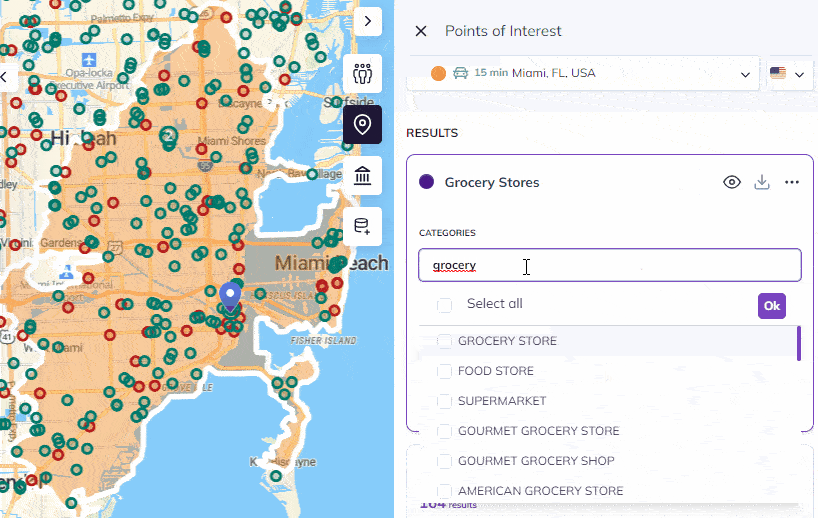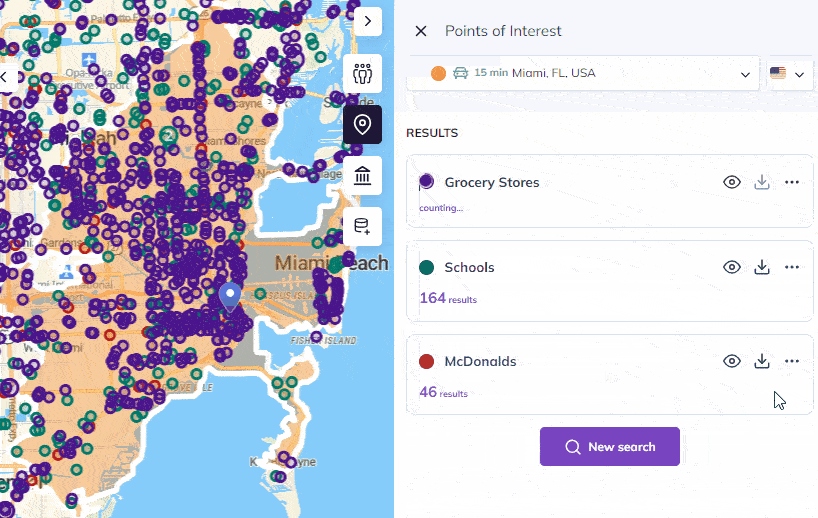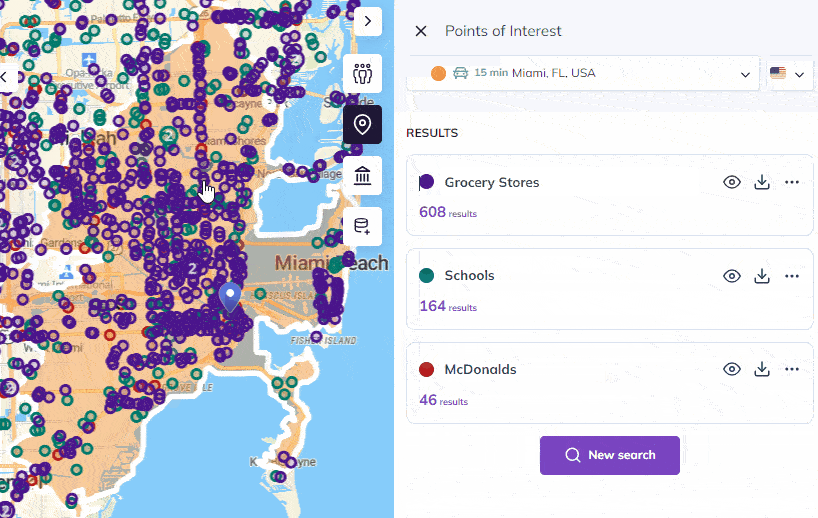
Beyond its approach, Smappen’s key strengths include its ability to create, manage, and visualize catchment areas efficiently, which is vital for assessing business attractiveness and geographical coverage, especially for those operating in a network of stores or services. Additionally, Smappen provides access to valuable population data, sourced from the INSEE census in France, enabling users to delve into demographics such as gender, age, socioeconomic status, and housing within their catchment areas.
The software’s ability to import and analyze customer data offers crucial insights into market penetration, helping users answer essential questions about their customer base. Smappen’s track record as a market leader in the franchise industry, serving over 200 franchisor clients, further underlines its effectiveness in providing solutions that meet the diverse needs of businesses and networks across various sectors.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur, a business owner, or a professional in urban planning, environmental management, or any field where spatial data is essential, Smappen stands as a reliable and adaptable GIS software solution to support your needs and drive data-driven decision-making.
Try smappen, the most intuitive and easiest-to-use GIS on the market.
Start your analysis, make better decisions, map your customers and plot your competitors in a matter of minutes.
Future Trends in GIS
The realm of Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is in a constant state of evolution, with the technology opening new frontiers for innovation and exploration. As we look to the future, several trends are shaping the landscape of GIS technology, promising exciting possibilities.
One prominent trend is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into GIS. AI empowers GIS systems to process vast amounts of data more intelligently, enhancing the accuracy and speed of geospatial analysis. Machine learning algorithms can detect patterns, predict outcomes, and even automate data collection, making GIS an even more powerful tool for decision-makers in various industries.
3D mapping is another transformative trend, taking GIS to new heights—quite literally. By extending beyond two dimensions into the third dimension, GIS can provide more comprehensive and immersive spatial representations. This trend is particularly valuable for urban planning, architecture, and environmental modeling, as it allows stakeholders to visualize complex landscapes in a more detailed and realistic manner.
The advent of mobile GIS applications is yet another remarkable development. As mobile devices become increasingly powerful and ubiquitous, GIS software is now accessible on smartphones and tablets. This mobile capability allows field workers to collect and analyze data in real-time, contributing to more agile and responsive decision-making.
These trends, among others, are shaping the future of GIS technology, offering boundless opportunities for those who harness its potential. As GIS continues to evolve, it promises to deliver even more comprehensive, efficient, and insightful solutions for a multitude of industries and applications.
What is the difference between GIS and GPS?
GPS, or the “Global Positioning System”, amounts to coordinates that give the location of a thing, place, or person. A GIS, on the other hand, is a software package that processes location data (like GPS coordinates) on a map. GISs are used to get a better understanding and visual representation of geospatial data.

I have been searching for this software for years! smappen is nothing short of incredible. It is exactly what I needed and produces fantastic results. And the user interface… It is so simple!

I manage 25 territories across the US for medical device sales distribution. Mapping territories for my reps has never been easier. smappen turned me into a hero at the company!

Exceptional and personal training and support. It did exactly what I wanted it to do, with a very high degree of accuracy.
Start using smappen now
